商品详情
返回产品目录商品包装及说明书因厂家更换频繁,如有不符以实物为主
奥利司他胶囊
国际零售参考价:¥**/盒
产品参数 中文说明 外文说明关联产品 本品资讯
-
- 通用名称
- 奥利司他胶囊
- 商品名
- 赛尼可
- 其它名称
- Xenical
- 英文名称
- Orlistat
- 包装规格
- 120mg×84粒
- 关键词
- 减肥药OTC
- 产地及厂家
- 上海罗氏制药有限公司
- 适应症范围
- 用于肥胖管理
-
温馨提醒:本说明书仅供参考,最新的说明书详见药品附带的说明书。
1 适应症和用法
XENICAL适用于肥胖管理,包括与低热量饮食结合使用时减轻体重和维持体重。XENICAL还表明可降低先前体重减轻后体重反弹的风险。XENICAL适用于初始体重指数 (BMI) ≥30 kg/m 2或≥27 kg/m 2且存在其他危险因素(例如,高血压、糖尿病、血脂异常)的肥胖患者。
表 1说明了根据各种体重和身高的体重指数 (BMI)。BMI 的计算方法是体重(公斤)除以身高(米)的平方。例如,体重 180 磅且身高 5 英尺5 英寸的人的 BMI 为 30。

2 剂量和给药方法
2.1 推荐剂量
XENICAL的推荐剂量是每天 3 次服用一粒120-mg 胶囊,每顿含脂肪的主餐(餐中或餐后 1 小时内)。
患者应采用营养均衡、低热量的饮食,其中大约 30% 的热量来自脂肪。脂肪、碳水化合物和蛋白质的每日摄入量应分布在三餐中。如果偶尔错过一餐或不含脂肪,则可以省略XENICAL的剂量。
因为XENICAL已被证明会减少一些脂溶性维生素和 β-胡萝卜素的吸收,应建议患者服用含有脂溶性维生素的多种维生素以确保足够的营养 [见 警告和注意事项 (5.1) ] 。维生素补充剂应在服用XENICAL之前或之后至少 2 小时服用,例如在睡前服用。
对于同时接受XENICAL和环孢素治疗的患者,在XENICAL后 3 小时给予环孢素。
对于同时接受XENICAL和左旋甲状腺素治疗的患者,应至少间隔 4 小时服用左旋甲状腺素和XENICAL。应监测同时使用XENICAL和左旋甲状腺素治疗的患者甲状腺功能的变化。
每天 3 次超过 120 毫克的剂量尚未显示提供额外的好处。
根据粪便脂肪测量值,在给药后 24 至 48 小时即可看到XENICAL的效果。停止治疗后,粪便脂肪含量通常会在 48 至 72 小时内恢复到治疗前的水平。
3 剂型和规格
XENICAL 120 毫克绿松石胶囊,用黑色墨水印有XENICAL 120。
4 禁忌症
XENICAL禁用于:
- 怀孕 [见 在特定人群中使用 (8.1) ]
- 慢性吸收不良综合征患者
- 胆汁淤积患者
- 已知对XENICAL或本产品的任何成分过敏的患者
5 警告和注意事项
5.1 药物相互作用和维生素吸收降低
XENICAL可能与包括环孢素、左旋甲状腺素、华法林、胺碘酮、抗癫痫药和抗逆转录病毒药物在内的伴随药物相互作用 [见 药物相互作用(7) ]。
来自XENICAL和环孢菌素药物相互作用研究的数据表明,当XENICAL与环孢菌素共同给药时,环孢菌素血浆水平降低。因此,不应同时使用XENICAL和环孢素。为减少药物相互作用的机会,服用这两种药物的患者应在XENICAL之前或之后至少 3 小时服用环孢素。此外,对于那些正在测量环孢素水平的患者,应考虑更频繁地监测。
应强烈鼓励患者服用含有脂溶性维生素的复合维生素补充剂以确保充足的营养,因为XENICAL已被证明可减少某些脂溶性维生素和 β-胡萝卜素的吸收 [见 剂量和给药方法 (2)和 不良反应反应(6.1) ] 。此外,与非肥胖受试者相比,肥胖患者的维生素 D 和 β-胡萝卜素水平可能较低。补充剂应在XENICAL给药前后至少 2 小时每天服用一次,例如在睡前服用。
减肥可能会影响糖尿病患者的血糖控制。一些患者可能需要减少口服降血糖药物(例如磺脲类)或胰岛素的剂量 [见 临床研究 (14) ] 。
5.2 肝损伤
曾有罕见的上市后报告,表明接受XENICAL治疗的患者出现严重肝损伤并伴有肝细胞坏死或急性肝功能衰竭,其中一些病例导致肝移植或死亡。应指导患者在服用XENICAL 时报告任何肝功能障碍症状(厌食、瘙痒、黄疸、尿色深、大便呈浅色或右上腹痛)。当出现这些症状时,应立即停用XENICAL和其他可疑药物,并检测肝功能和 ALT 和 AST 水平。
5.3 尿草酸盐增加
一些患者在使用XENICAL治疗后可能会出现尿草酸盐水平升高。已有草酸盐肾结石和草酸盐肾病伴肾功能衰竭的病例报告。向有肾功能损害风险的患者开具XENICAL处方时监测肾功能,并在有高草酸尿症或草酸钙肾结石病史的患者中谨慎使用。
5.4 胆石症
大量体重减轻会增加胆石症的风险。在XENICAL预防 2 型糖尿病的临床试验中,随机分配至XENICAL 的患者胆石症作为不良事件的发生率为 2.9% (47/1649),随机分配至安慰剂的患者为 1.8% (30/1655)。
5.5 其他
在开出XENICAL之前,应排除肥胖的器质性原因(例如,甲状腺功能减退症)。
应建议患者遵守饮食指南 [见 剂量和给药方法 (2) ] 。当XENICAL与高脂肪饮食(> 30% 来自脂肪的每日总热量)一起服用时,胃肠道事件 [见 不良反应 (6.1) ] 可能会增加。脂肪的每日摄入量应分布在三餐主餐中。如果XENICAL与脂肪含量非常高的任何一餐一起服用,胃肠道反应的可能性就会增加。
6 不良反应
6.1 临床试验
因为临床试验是在广泛不同的条件下进行的,在一种药物的临床试验中观察到的不良反应率不能直接与另一种药物的临床试验中的发生率进行比较,并且可能无法反映在患者中观察到的发生率。
通常观察到(基于第一年和第二年的数据)
在七项双盲、安慰剂对照临床试验中,胃肠 (GI) 症状是最常观察到的与使用XENICAL相关的治疗出现的不良事件,并且主要是作用机制的一种表现。(通常观察到的定义为≥5% 的发生率和XENICAL 120 mg 组的发生率至少是安慰剂的两倍。)

一般来说,这些事件的第一次发生是在开始治疗的 3 个月内。总体而言,大约 50% 的与XENICAL治疗相关的所有胃肠道不良事件持续时间不到 1 周,大多数持续时间不超过 4 周。但是,某些人可能会在 6 个月或更长时间内发生胃肠道不良事件。
停止治疗
在对照临床试验中,8.8% 的XENICAL治疗患者因不良事件而停止治疗,而安慰剂治疗患者的这一比例为 5.0%。对于XENICAL,导致停止治疗的最常见不良事件是胃肠道。
其他不良临床事件
下表列出了来自七项多中心、双盲、安慰剂对照临床试验的其他治疗中出现的不良事件,这些事件在接受XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次治疗的患者中发生的频率≥2%,并且发生率更高无论与研究药物的关系如何,第 1 年和第 2 年都优于安慰剂。

表 4说明了在患者先前未接受维生素补充剂的研究中,在 1 年和 2 年的治疗期间,服用 XENICAL和安慰剂的成年患者在连续两次或多次就诊时出现低维生素水平的百分比。

表 5说明了在 1 年研究期间连续两次或两次以上就诊时出现低维生素水平的服用XENICAL和安慰剂的青少年患者的百分比。

在为期 4 年的 XENDOS 研究中,不良事件的一般模式与 1 年和 2 年研究报告的相似,第 1 年发生的胃肠相关不良事件的总发生率在 4 年中逐年下降时期。
在肥胖糖尿病患者的临床试验中,也观察到低血糖和腹胀。
儿科患者
在12 至 16 岁青少年患者中使用XENICAL 的临床试验中,不良反应的概况与在成人中观察到的大致相似。
6.2 售后体验
在XENICAL 的批准后使用期间已确定以下不良反应。因为这些反应是从数量不确定的人群中自愿报告的,所以并不总是能够可靠地估计它们的频率或建立与XENICAL暴露的因果关系。
- 罕见的转氨酶升高和碱性磷酸酶升高以及肝炎可能很严重的病例已有报道。曾有在上市后监测中使用XENICAL观察到肝功能衰竭的报告,其中一些病例导致肝移植或死亡 [见 警告和注意事项 (5.2) ] 。
- 据报道,使用XENICAL会出现罕见的超敏反应。体征和症状包括瘙痒、皮疹、荨麻疹、血管性水肿、支气管痉挛和过敏反应。已经报道了非常罕见的大疱性喷发病例。
- 罕见的白细胞碎裂性血管炎病例已有报道。临床症状包括可触及的紫癜、斑丘疹或大疱性皮疹。
- 已有肾病患者或有肾病风险的患者在用XENICAL治疗后发生急性草酸盐肾病的报告 [见 警告和注意事项 (5.3) ] 。
- 已有在上市后监测中使用赛尼可引起胰腺炎的报告。尚未明确确定胰腺炎和肥胖症治疗之间的因果关系或病理生理机制。
- 据报道,在接受XENICAL治疗的患者中出现下消化道出血。大多数报告都是不严肃的;应进一步调查严重或持续的病例。
7 药物相互作用
7.1 环孢素
来自XENICAL和环孢菌素药物相互作用研究的数据表明,当XENICAL与环孢菌素共同给药时,环孢菌素血浆水平降低。XENICAL和环孢素不应同时服用。环孢素应在XENICAL 给药后 3 小时给药[见 剂量和给药方法 (2),以及 警告和注意事项 (5.1) ] 。
7.2 脂溶性维生素补充剂和类似物
来自药代动力学相互作用研究的数据表明,当与XENICAL 一起给药时,β-胡萝卜素补充剂的吸收会降低。XENICAL抑制了维生素 E 醋酸盐补充剂的吸收。目前尚不清楚 XENICAL对补充维生素 D、维生素 A 和营养衍生维生素 K 吸收 的影响[见 临床药理学 (12.3)和 警告和注意事项 (5.1) ] 。
7.3 左旋甲状腺素
在上市后与XENICAL和左旋甲状腺素同时治疗的患者中曾报道过甲状腺功能减退症。应监测同时使用XENICAL和左旋甲状腺素治疗的患者甲状腺功能的变化。给予左旋甲状腺素和XENICAL至少相隔 4 小时 [见 剂量和给药方法 (2) ] 。
7.4 包括华法林在内的抗凝剂
XENICAL可能会降低维生素 K 的吸收。据报道,在同时使用XENICAL和抗凝剂治疗的患者中,凝血酶原减少、INR 增加和抗凝剂治疗不平衡导致止血参数改变。服用XENICAL处方的长期稳定剂量华法林或其他抗凝剂的患者应密切监测凝血参数的变化 [见 临床药理学 (12.3) ] 。
7.5 胺碘酮
一项药代动力学研究,其中在奥利司他治疗期间口服给予胺碘酮,证明对胺碘酮及其代谢物去乙基胺碘酮的暴露减少 [见 临床药理学(12.3) ] 。胺碘酮的治疗效果可能会降低。尚未研究患者开始奥利司他治疗对稳定胺碘酮治疗的影响。
7.6 抗癫痫药
据报道,同时服用奥利司他和抗癫痫药的患者会出现惊厥。应监测患者抽搐频率和/或严重程度的可能变化。
7.7 抗逆转录病毒药物
据报道,在服用奥利司他与抗逆转录病毒药物如阿扎那韦、利托那韦、富马酸替诺福韦酯、恩曲他滨以及洛匹那韦/利托那韦和恩曲他滨/依法韦仑/替诺福韦酯的组合的 HIV 感染患者中,病毒学控制丧失。其确切机制尚不清楚,但可能包括抑制抗逆转录病毒药物全身吸收的药物相互作用。在接受 HIV 感染治疗期间服用XENICAL 的患者中,应经常监测 HIV RNA 水平。如果确认 HIV 病毒载量增加,则应停用XENICAL。
8 在特定人群中的使用
8.1 怀孕
怀孕类别 X
XENICAL在怀孕期间是禁忌的,因为减肥对孕妇没有潜在的好处,并且可能会导致胎儿受到伤害。由于怀孕期间母体组织必须增加体重,因此目前建议所有孕妇(包括已经超重或肥胖的孕妇)体重增加最少,且不减轻体重。在接受比推荐人用剂量高得多的剂量奥利司他的动物中,未观察到胚胎毒性或致畸性。如果在怀孕期间使用该药,或者如果患者在服用该药时怀孕,应告知患者母体体重减轻对胎儿的潜在危害。
动物数据
在大鼠和兔中以高达 800 mg/kg/天的剂量进行生殖研究。两项研究均未显示胚胎毒性或致畸性。该剂量分别是按体表面积 (mg/m 2 ) 计算的大鼠和兔每日人体剂量的 23 倍和 47 倍 。
8.3 哺乳母亲
尚不清楚XENICAL是否存在于人乳中。给哺乳期妇女服用XENICAL时应谨慎。
8.4 儿科使用
尚未确定 12 岁以下儿童患者的安全性和有效性。
XENICAL的安全性和有效性已在 12 至 16 岁的肥胖青少年患者中进行了评估。使用XENICAL在这个年龄组是从充分和良好对照的研究证据支持XENICAL在从54周的疗效和安全性研究的额外数据成人和肥胖青少年患者年龄在12到16之间的21天的矿物质平衡研究年。在为期 54 周的疗效和安全性研究中,接受XENICAL治疗的患者(64.8% 女性、75% 白种人、18.8% 黑人和 6.3% 其他人)的 BMI 平均降低 0.55 kg/m 2 ,而平均增加 0.31公斤/米 2在安慰剂治疗的患者中(p=0.001)。在这两项青少年研究中,不良反应通常与成人中描述的相似,包括脂肪/油性粪便、油性斑点和油性排泄。在来自 54 周研究的 152 名XENICAL和 77 名安慰剂患者的亚组中,DEXA 测量的身体成分变化在两个治疗组中相似,但脂肪量除外,与接受治疗的患者相比,接受XENICAL治疗的患者显着减少与安慰剂(-2.5 kg vs -0.6 kg,p=0.033)。因为赛尼可会干扰脂溶性维生素的吸收,所有患者都应每天服用含有维生素 A、D、E、K 和 β-胡萝卜素的多种维生素。维生素补充剂应在XENICAL 之前或之后至少 2 小时服用[见 剂量和给药方法 (2)、 警告和注意事项 (5.1)和 临床药理学 (12.3) ] 。
奥利司他及其代谢物 M1 和 M3 的血浆浓度与在相同剂量水平下在成人中发现的浓度相似。在XENICAL和安慰剂治疗组中,每日粪便脂肪排泄量分别占膳食摄入量的 27% 和 7% 。
8.5 老年人使用
XENICAL 的临床研究没有包括足够数量的 65 岁及以上患者来确定他们的反应是否与年轻患者不同 [见 临床研究 (14) ] 。
9 药物滥用和依赖
9.2 滥用
与任何减肥药一样,在不适当的患者群体(例如,神经性厌食症或贪食症患者)中存在滥用XENICAL的可能性。有关推荐的处方指南,请参阅 适应症和用法 (1)。
10 药物过量
已经在正常体重和肥胖受试者中研究了单剂量 800 毫克XENICAL和多剂量高达 400 毫克,每天 3 次,共 15 天,没有明显的不良发现。
如果发生显着过量的XENICAL,建议对患者观察 24 小时。根据人类和动物研究,归因于XENICAL的脂肪酶抑制特性的全身效应应该是快速可逆的。
11 说明
XENICAL(奥利司他)是一种用于肥胖管理的胃肠道脂肪酶抑制剂,通过抑制膳食脂肪的吸收起作用。
奥利司他是 (S)-2-formylamino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid (S)-1-[[(2S, 3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl] 甲基]-十二烷基酯。其经验式为C 29 H 53 NO 5,分子量为495.7。它是包含四个手性中心的单个非对映异构分子,在乙醇中在 529 nm 处具有负旋光度。结构是:
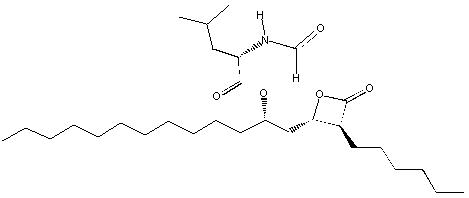
奥利司他是一种白色至灰白色结晶粉末。奥利司他几乎不溶于水,易溶于氯仿,极易溶于甲醇和乙醇。奥利司他在生理pH范围内没有p K a。
XENICAL可作为绿松石硬明胶胶囊口服给药。胶囊印有黑色。每个胶囊含有由 120 mg 活性成分奥利司他以及非活性成分微晶纤维素、羟基乙酸淀粉钠、十二烷基硫酸钠、聚维酮和滑石粉组成的丸剂。胶囊壳含有明胶、二氧化钛和FD&C Blue No. 2,黑色印刷油墨含有药用级虫胶、丙二醇、强铵溶液、氢氧化钾和黑色氧化铁。
12 临床药理学
12.1 作用机制
奥利司他是胃肠道脂肪酶的可逆抑制剂。它通过与胃和胰脂肪酶的活性丝氨酸残基位点形成共价键,在胃和小肠腔内发挥治疗活性。因此,失活的酶不能将甘油三酯形式的膳食脂肪水解成可吸收的游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯。由于未消化的甘油三酯不被吸收,由此产生的热量不足可能对体重控制产生积极影响。
12.2 药效学
剂量反应关系
奥利司他在人类志愿者中的剂量反应关系如图 1所示 。效果是摄入脂肪排出的百分比,简称粪便脂肪排出百分比。图 1显示了个体数据(空心圆圈)和使用最大效应模型(实线)为群体预测的曲线 。
图 1 奥利司他在人类志愿者中的剂量-反应关系
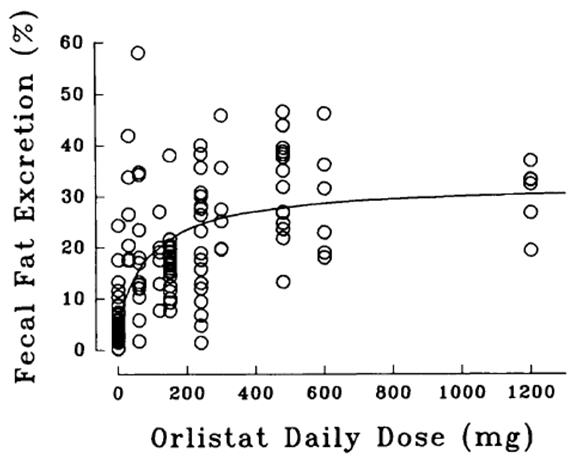
在推荐的治疗剂量 120 毫克,每天 3 次时,奥利司他可抑制约 30% 的膳食脂肪吸收。
乙醇不影响奥利司他阻止脂肪吸收的作用。
其他短期研究
成年人
在几项持续时间长达 6 周的研究中,在正常体重和肥胖受试者中评估了治疗剂量的赛尼可对胃肠道和全身生理过程的影响。在两项研究中,多次服用XENICAL后餐后胆囊收缩素血浆浓度降低,但在另外两项实验中与安慰剂没有显着差异。在胆囊运动、胆汁成分或成石性或结肠细胞增殖率方面没有观察到临床上显着的变化,胃排空时间或胃酸度没有临床上显着的减少。此外,没有观察到XENICAL对血浆甘油三酯水平或全身脂肪酶的影响在这些研究中。在对 28 名健康男性志愿者进行的为期 3 周的研究中,XENICAL(120 毫克,每天 3 次)没有显着影响钙、镁、磷、锌、铜和铁的平衡。
儿科
在对 32 名 12 至 16 岁的肥胖青少年进行的为期 3 周的研究中,XENICAL(120 毫克,每天 3 次)没有显着影响钙、镁、磷、锌或铜的平衡。在XENICAL和安慰剂治疗组中,铁平衡分别降低了 64.7 µmole/24 小时和 40.4 µmole/24 小时。
12.3 药代动力学
吸收
奥利司他的全身暴露是最小的。口服 360 mg 14 C-奥利司他后,血浆放射性在大约 8 小时达到峰值;完整奥利司他的血浆浓度接近检测限 (<5 ng/mL)。在涉及监测血浆样本的治疗研究中,血浆中完整奥利司他的检测是零星的,浓度很低(<10 ng/mL 或 0.02 µM),没有积累的证据,并且与最小吸收一致。
分配
体外奥利司他与血浆蛋白的结合率 > 99%(脂蛋白和白蛋白是主要的结合蛋白)。奥利司他最低限度地分成红细胞。
代谢
基于口头 14肥胖患者中的 C-奥利司他质量平衡研究,两种代谢物 M1((奥利司他的水解 β-内酯环产物)和 M3(M1 裂解 N-甲酰基亮氨酸侧链后的连续代谢物)约占 42% M1 和 M3 具有开放的 β-内酯环和极弱的脂肪酶抑制活性(分别比奥利司他低 1000 倍和 2500 倍)。鉴于这种低抑制活性和低血浆水平治疗剂量(给药后 2 至 4 小时,M1 和 M3 的平均值分别为 26 ng/mL 和 108 ng/mL),这些代谢物被认为在药理学上无关紧要。主要代谢物 M1 的半衰期很短(大约 3小时),而次生代谢物 M3 的消除速度较慢(半衰期约为 13.5 小时)。
消除
在正常体重和肥胖受试者中单次口服 360 mg 14 C-奥利司他后,发现未吸收药物的粪便排泄是主要的消除途径。奥利司他及其 M1 和 M3 代谢物也受胆汁排泄。大约 97% 的放射性物质通过粪便排出;发现其中 83% 的奥利司他未发生变化。总放射性的累积肾脏排泄量 < 360 mg 给定剂量的 2% 14C-奥利司他。达到完全排泄(粪便加尿)的时间为 3 至 5 天。正常体重和肥胖受试者之间奥利司他的倾向似乎相似。根据有限的数据,被吸收的奥利司他的半衰期在 1 到 2 小时之间。
特定人群
没有对特定人群进行药代动力学研究,例如老年人、不同种族以及肾和肝功能受损的患者。
药物相互作用
酒精
在 30 名正常体重受试者的多剂量研究中,同时服用XENICAL和40 克酒精(例如,大约 3 杯酒)不会导致酒精药代动力学、奥利司他药效学(粪便脂肪排泄)或全身暴露的改变奥利司他。
胺碘酮
在一项对健康志愿者进行的药代动力学研究中,他们每天服用 3 次 120 毫克奥利司他,共 13 天,并在第 14 天早上单次服用 120 毫克奥利司他,并在第 4 天服用单剂 1200 毫克胺碘酮,结果显示 23 – 观察到胺碘酮和去乙基胺碘酮的全身暴露减少 27% [见 药物相互作用 (7.5) ] 。尚未研究患者开始奥利司他治疗对稳定胺碘酮治疗的影响。
环孢素
在一项多剂量研究中,每天2次50 mg 环孢菌素与每天 3 次120 mg XENICAL共同给药使环孢菌素 AUC 和 C max 分别降低 31% 和 25%。在同一研究中,在每天3次服用120 mg XENICAL后 3 小时每天服用 50 mg 环孢菌素使环孢菌素 AUC 和 C max 分别降低 17% 和 4%。
地高辛
在 12 名接受XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次共 6 天的正常体重受试者中,XENICAL没有改变单剂量地高辛的药代动力学。
脂溶性维生素补充剂和类似物
一项药代动力学相互作用研究表明,与XENICAL 合用时,β-胡萝卜素补充剂的吸收减少了 30% 。XENICAL抑制了大约 60% 的维生素 E 醋酸盐补充剂的吸收。目前尚不清楚 XENICAL对补充维生素 D、维生素 A 和营养衍生维生素 K 吸收的影响。
格列本脲
在 12 名接受奥利司他 80 mg 每天 3 次共 5 天的正常体重受试者中,奥利司他没有改变格列本脲的药代动力学或药效学(降血糖)。
硝苯地平(缓释片)
在 17 名接受XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次共 6 天的正常体重受试者中,XENICAL没有改变硝苯地平(缓释片)的生物利用度。
口服避孕药
在 20 名体重正常的女性受试者中,服用XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次,共 23 天,口服避孕药的排卵抑制作用没有变化。
苯妥英
在 12 名接受XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次共 7 天的12 名正常体重受试者中,XENICAL没有改变单剂量 300-mg 苯妥英的药代动力学。
普伐他汀
在 24 名正常体重、轻度高胆固醇血症患者接受XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次共 6 天的双向交叉研究中,XENICAL不影响普伐他汀的药代动力学。
华法林
在 12 名正常体重受试者中,每天 3 次服用XENICAL 120 mg 共 16 天,不会导致华法林药代动力学(R-和 S-对映异构体)或药效学(凝血酶原时间和血清因子 VII)发生任何变化。虽然羧基化不足的骨钙素(维生素 K 营养状况的标志物)在服用XENICAL后未发生改变,但服用XENICAL 的受试者的维生素 K 水平趋于下降。因此,由于XENICAL可能会降低维生素 K 的吸收,因此应密切监测服用XENICAL长期稳定剂量华法林的患者的凝血参数变化。
13 非临床毒理学
13.1 致癌作用、诱变作用、生育力受损
大鼠和小鼠的致癌性研究未显示奥利司他分别高达 1000 mg/kg/天和 1500 mg/kg/天的致癌潜力。对于小鼠和大鼠,这些剂量是人体每日剂量的 38 和 46 倍,根据药物相关物质总量的浓度与时间曲线下面积计算得出。
根据艾姆斯试验、哺乳动物正向突变试验 (V79/HPRT)、外周人淋巴细胞的体外断裂发生试验、培养的大鼠肝细胞中的计划外 DNA 合成试验 (UDS),奥利司他没有可检测的诱变或基因毒性活性,和体内小鼠微核试验。
在生育和生殖研究中以 400 毫克/公斤/天的剂量给予大鼠时,奥利司他没有观察到的副作用。该剂量是按体表面积 (mg/m 2 )计算的人体每日剂量的 12 倍 。
14 临床研究
XENICAL对与肥胖相关的发病率和死亡率的长期影响尚未确定。
在为期4 年的 XENDOS 研究和七个长期 (1- 2 年)多中心、双盲、安慰剂对照临床试验。在治疗的第一年,为期 2 年的研究评估了体重减轻和体重维持情况。在治疗的第二年,一些研究评估了持续的体重减轻和体重维持,而其他研究则评估了XENICAL对体重恢复的影响。这些研究包括超过 2800 名接受XENICAL治疗的患者1400 名接受安慰剂治疗的患者(年龄范围 17-78 岁,80.2% 女性,91.0% 白种人,5.7% 黑人,2.3% 西班牙裔,0.9% 其他)。这些患者中的大多数有肥胖相关的危险因素和合并症。在 XENDOS 研究中,包括 3304 名患者(年龄范围 30-58 岁,女性占 55%,白种人占 99%,其他人占 1%),除了体重管理外,还评估了 2 型糖尿病的发病时间。在所有这些研究中,XENICAL和安慰剂治疗分别表示XENICAL加饮食和安慰剂加饮食治疗。
在减肥和维持体重期间,向所有患者推荐均衡、低热量的饮食,旨在使热量摄入减少约 20% 并提供 30% 的脂肪热量。此外,所有患者都接受了营养咨询。
14.1 一年结果:减肥、维持体重和风险因素
来自五项临床试验的汇总数据表明,在意向治疗人群中,从随机分组到治疗 1 年结束的总体平均体重减轻,在接受XENICAL治疗的患者中为 13.4 磅,在接受安慰剂治疗的患者中为 5.8 磅。治疗 1 年后,XENICAL治疗的患者和安慰剂治疗的患者之间的平均体重减轻百分比差异为 3%。172名 (69%) 接受XENICAL治疗的患者和 701 名 (63%) 接受安慰剂治疗的患者完成了 1 年的治疗。在完成 1 年治疗的患者中,57% 的接受XENICAL(120 毫克,每天 3 次)治疗的患者和 31% 的安慰剂治疗患者至少减轻了基线体重的 5%。
在针对意向治疗人群的五项大型多中心研究中,1 年后体重减轻≥5% 和≥10% 的患者百分比 见表 6。

在使用XENICAL和安慰剂治疗 1 年后,与肥胖相关的危险因素的相对变化针对整个人群和随机化时具有异常值的人群呈现。
总体人口
根据五项临床研究的汇总数据,与肥胖相关的代谢、心血管和人体测量风险因素的变化,无论患者在随机化时的风险因素状态如何,均列于 表 7 中。一年的XENICAL治疗导致几个危险因素的相对改善。

随机化时具有异常危险因素的人群
在具有异常脂质水平(LDL ≥ 130 mg/dL,LDL/HDL ≥3.5,HDL <35 mg/dL)的人群中,在 LDL-胆固醇方面,与安慰剂相比,XENICAL治疗 1 年后随机化的变化更大(-7.83% vs +1.14%) 和 LDL/HDL 比率 (-0.64 vs -0.46)。安慰剂组的 HDL 增加了 20.1%,XENICAL组增加了 18.8%。在基线血压异常(收缩压≥ 140 mmHg)的人群中,XENICAL(-10.89 mmHg)从随机化到 1 年的 SBP 变化大于安慰剂(-5.07 mmHg)。对于舒张压≥90 mm Hg 的患者,XENICAL患者减少了 -7.9 毫米汞柱,而安慰剂患者减少了 -5.5 毫米汞柱。在基线值异常 (≥120 pmol/L) 的人群中,从随机分组到 1 年,XENICAL 的空腹胰岛素下降幅度大于安慰剂 (-39 vs -16 pmol/L)。在基线值异常 (≥100 cm) 的人群中,观察到XENICAL与安慰剂相比,腰围的减少幅度更大(-7.29 vs -4.53 cm)。
14.2 对体重恢复的影响
三项研究旨在评估XENICAL与安慰剂相比在减少先前单独饮食(一项研究,14302)或先前使用XENICAL治疗(两项研究,14119C 和 14185)后体重减轻后体重反弹的效果。在研究的 1 年体重恢复部分期间使用的饮食是维持体重的饮食,而不是减肥饮食,与减肥研究中的患者相比,患者接受的营养咨询较少。对于研究 14119C 和 14185,患者之前的体重减轻是由于 1 年的XENICAL治疗与轻度低热量饮食相结合。进行 14302 研究以评估使用XENICAL治疗 1 年的效果 在过去 6 个月内仅通过节食减掉 8% 或更多体重的患者的体重反弹。
在研究 14119C 中,接受安慰剂治疗的患者恢复了之前减掉的 52% 的体重,而接受XENICAL治疗的患者恢复了之前减掉的 26%(p<0.001)。在研究 14185 中,接受安慰剂治疗的患者体重恢复了之前减掉的 63%,而接受XENICAL治疗的患者减掉了 35%(p<0.001)。在研究 14302 中,接受安慰剂治疗的患者恢复了之前减掉的 53% 的体重,而接受XENICAL治疗的患者恢复了减掉的32%(p<0.001)。
14.3 两年结果:长期体重控制和风险因素
在之前讨论的五项为期 1 年的体重管理临床研究中的四项中,对XENICAL的治疗效果进行了为期 2 年的检查( 见表 6)。在第 1 年结束时,对患者的饮食进行审查并在必要时进行更改。第二年规定的饮食旨在保持患者目前的体重。在四项大型、多中心、2 年双盲、安慰剂对照研究中,XENICAL被证明在长期体重控制方面比安慰剂更有效。
来自四项临床研究的汇总数据表明,74% 接受 120 mg 每天 3 次XENICAL治疗的患者和 76% 接受安慰剂治疗的患者完成了 2 年的相同治疗。来自四项临床研究的汇总数据表明,在完成 1 年治疗 (ITT LOCF) 的患者中,XENICAL 120 mg 每天 3 次与安慰剂治疗组在第 2 年之间的平均体重减轻差异为 3%。在一年结果( 见表 6)中引用的相同研究 中,表 8显示了 2 年后体重减轻 ≥ 5% 和 ≥ 10% 的患者百分比 。

治疗 2 年后与肥胖相关的危险因素的相对变化也在整个人群和随机化时具有异常危险因素的人群中进行了评估。
总体人口
XENICAL和安慰剂治疗之间风险因素的相对差异与治疗1 年后的总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白/高密度脂蛋白比率、甘油三酯、空腹血糖、空腹胰岛素、舒张压、腰围、和臀围。高密度脂蛋白胆固醇和收缩压治疗组之间的相对差异小于第一年结果中观察到的差异。
随机化时具有异常危险因素的人群
XENICAL和安慰剂治疗之间风险因素的相对差异与LDL- 和 HDL-胆固醇、甘油三酯、空腹胰岛素、舒张压和腰围治疗 1 年后的结果相似。治疗组之间 LDL/HDL 比率和孤立收缩压的相对差异小于第一年结果中观察到的差异。
14.4 四年结果:长期体重控制和风险因素
在为期 4 年的双盲、安慰剂对照 XENDOS 研究中,在 3304 名基线时糖耐量正常或受损的肥胖患者中,将XENICAL延迟 2 型糖尿病发病和对体重的影响与安慰剂进行了比较。随机分配到安慰剂组的 1655 名患者中的 34% 和随机分配到XENICAL组的1649 名患者中的 52%完成了为期 4 年的研究。
在研究结束时,安慰剂组的平均体重减轻百分比为 -2.75%,而XENICAL组为 -5.17% (p<0.001)(参见 图2)。45% 的安慰剂患者和 73% 的XENICAL患者减少了 ≥ 5% 的基线体重,21% 的安慰剂患者和 41% 的XENICAL患者减少了 ≥ 10% 的基线体重。治疗的第一年。经过 4 年的治疗,28% 的安慰剂患者和 45% 的XENICAL患者失去了 ≥ 5% 的基线体重,10% 的安慰剂患者和 21% 的XENICAL患者失去了 ≥ 10% 的基线体重重量。经过 4 年的治疗,XENICAL治疗患者和安慰剂之间体重减轻的平均百分比差异为 2.5%。
图 2 基线体重 (Kgs) 随时间的平均变化*
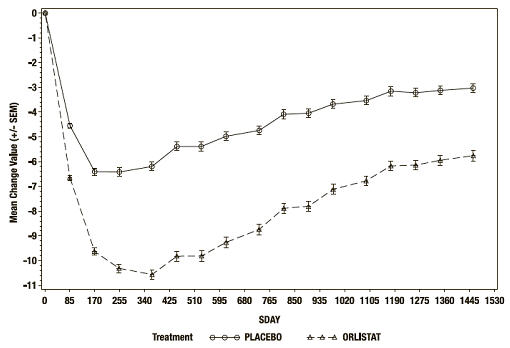
*ITT LOCF 研究人群
在 XENDOS 研究人群中评估了治疗 4 年后与肥胖相关的危险因素相对于基线的相对变化(见 表 9 )。

肥胖患者 2 型糖尿病的发作
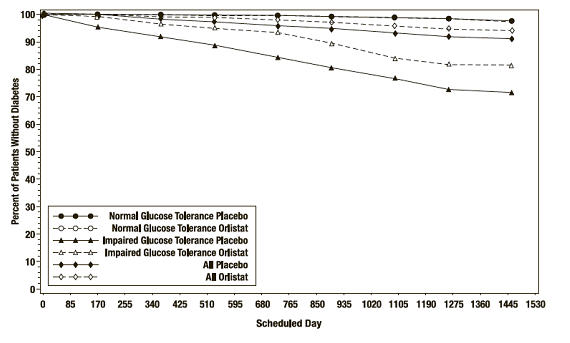
在 XENDOS 试验中,在总体人群中,XENICAL延迟了 2 型糖尿病的发病,因此在四年治疗结束时,安慰剂组的糖尿病累积发病率为 8.3%,而XENICAL组为 5.5% , p=0.01( 见表10)。这一发现是由于在基线时糖耐量受损的患者中发生 2 型糖尿病的发生率在统计学上显着降低( 表 10和 图 3)。XENICAL并未降低基线时葡萄糖耐量正常的患者发生糖尿病的风险。
XENICAL延迟肥胖 IGT 患者 2 型糖尿病发病的作用可能是由于体重减轻,而不是药物对葡萄糖或胰岛素代谢的任何独立影响。XENICAL对减肥的影响是辅助饮食和运动的。

图 3 无糖尿病患者的百分比随时间推移
14.5 2 型糖尿病患者的研究
对磺脲类药物稳定的 2 型糖尿病患者 (N=321) 进行了为期 1 年的双盲、安慰剂对照研究。与安慰剂治疗患者的 13% 相比,30% 的接受XENICAL治疗的患者从随机分组中获得了至少 5% 或更多的体重减轻(p<0.001)。 表 11描述了与安慰剂相比,XENICAL治疗 1 年期间在磺脲类药物使用和剂量减少以及血红蛋白 HbA1c、空腹血糖和胰岛素方面的变化。

此外,与安慰剂(n=159)相比,XENICAL(n=162)与总胆固醇(-1.0% 对 +9.0%,p≤0.05)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(-3.0% 对 +10.0%)的显着降低相关, p≤0.05), LDL/HDL 比值 (-0.26 vs -0.02, p≤0.05) 和甘油三酯 (+2.54% vs +16.2%, p≤0.05)。对于 HDL 胆固醇,XENICAL增加了 +6.49% ,安慰剂增加了 +8.6%,p>0.05。收缩压增加0.61毫米汞柱上XENICAL和安慰剂组,P> 0.05增加4.33毫米汞柱。XENICAL 的舒张压降低了 -0.47 毫米汞柱,安慰剂降低了-0.5 毫米汞柱,p>0.05。
14.6 肥胖患者的葡萄糖耐受性
包括口服葡萄糖耐量试验在内的为期两年的研究是在先前未诊断或接受过 2 型糖尿病治疗且随机分组时基线口服葡萄糖耐量试验 (OGTT) 状态为正常、受损或糖尿病的肥胖患者中进行的。
比较了在用XENICAL (n=251) 或安慰剂 (n=207)治疗 2 年后从随机化时的正常 OGTT 到糖尿病或受损的 OGTT 的进展。用XENICAL治疗后,分别有0.0% 和 7.2% 的患者从正常进展到糖尿病和从正常进展到受损,而安慰剂治疗组分别为 1.9% 和 12.6%。
在随机分组时发现 OGTT 受损的患者中,显示了与安慰剂相比,在接受XENICAL治疗 1 年和 2 年后,患者改善至正常或恶化为糖尿病状态的百分比。治疗 1 年后,45.8% 的安慰剂患者和 73% 的XENICAL患者口服葡萄糖耐量试验正常,而 10.4% 的安慰剂患者和 2.6% 的XENICAL患者患有糖尿病。治疗 2 年后,50% 的安慰剂患者和 71.7% 的XENICAL患者口服葡萄糖耐量试验正常,而 7.5% 的安慰剂患者和 1.7% 的XENICAL患者在治疗后发现患有糖尿病.
14.7 儿科临床研究
在一项为期 54 周的多中心、双盲、安慰剂对照研究中评估了XENICAL对体重指数 (BMI) 和体重减轻的影响,该研究对 539 名肥胖青少年(357 名接受XENICAL 120 毫克每天三次,182 名接受安慰剂),年龄在 12 至 16 岁之间。所有研究参与者的基线 BMI 比美国基于年龄和性别的第95个百分位数的加权平均值高 2 个单位 。体重指数是主要的疗效参数,因为它考虑了成长中儿童身高和体重的变化。
在研究期间,所有患者都被指示在摄入XENICAL之前或之后至少 2 小时服用含有脂溶性维生素的复合维生素。患者还保持均衡、低热量的饮食,旨在提供 30% 的卡路里来自脂肪。此外,所有患者都接受了行为矫正计划并提供了运动咨询。
每个治疗组中大约 65% 的患者完成了研究。
治疗一年后,XENICAL治疗患者的BMI 平均下降 0.55 kg/m 2,安慰剂治疗患者的BMI 平均下降 0.31 kg/m 2 (p=0.001)。
意向治疗人群在治疗 52 周后 BMI 和体重降低≥5% 和≥10% 的患者百分比 见表 12。

16 如何供应/储存和处理
XENICAL是一种含有粉末颗粒的绿松石硬明胶胶囊。
XENICAL 120 毫克胶囊:绿松石,两件式,1 号不透明硬明胶胶囊,黑色墨水印有XENICAL 120 — 90 瓶 (NDC 61269-460-90)。
储存和处理
储存在 25°C (77°F);允许在 15° 至 30°C(59° 至 86°F)范围内移动 [参见 USP 控制室温]。保持瓶子紧闭。
在给定的失效日期之后不应使用XENICAL。
17 患者咨询信息
请参阅 FDA 批准的患者标签(患者信息)。
患者信息
如果怀孕、患有慢性吸收不良综合征、胆汁淤积或对XENICAL或本产品的任何成分 过敏的患者不应服用XENICAL [见 禁忌症 (4) ] 。
伴随药物
由于潜在的相互作用,应询问患者是否正在服用环孢素、β-胡萝卜素或维生素 E 补充剂、左旋甲状腺素、华法林、抗癫痫药、胺碘酮或抗逆转录病毒药物 [见 药物相互作用 (7) ] 。
常见的不良事件
应告知患者常见观察到的与使用XENICAL相关的不良事件,包括油斑、排气伴排出物、大便急迫、脂肪/油性粪便、油性排便、排便增加、大便失禁 [见 不良反应 (6.1) ] .
潜在风险和收益
应告知患者潜在风险,包括脂溶性维生素吸收降低和潜在肝损伤、尿草酸盐增加和胆石症 [见 警告和注意事项 (5) ] 。用XENICAL治疗可能会导致体重减轻和因体重减轻而导致的肥胖相关危险因素的改善 [见 临床研究 (14) ] 。
给药说明
应建议患者在进餐时或餐后 1 小时内按照指示服用XENICAL。还应建议患者在XENICAL给药前或给药后至少两小时或在睡前服用 复合维生素补充剂[见 剂量和给药方法 (2) ] 。
XENICAL ® 是CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH 的注册商标。
许可方:
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH
Ziegelhof 24
17489 Greifswald, Germany
经销:
H2-Pharma, LLC
2010 Berry Chase Place
Montgomery, AL 36117, USA
© 2017 CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH。版权所有。患者信息
XENICAL ® (zen´i-cal)
( orlistat )
胶囊在您开始服用XENICAL之前以及每次补充药物时,请阅读此患者信息。可能有新的信息。此信息不能代替与您的医生讨论您的健康状况或治疗。
什么是赛尼可?
XENICAL是一种处方药,用于低热量饮食,以增加肥胖人群的体重减轻。XENICAL可帮助肥胖者减轻体重并保持体重减轻。
尚不清楚XENICAL对 12 岁以下儿童是否安全有效。
谁不应该服用XENICAL?
如果您有以下情况,请勿服用XENICAL:
- 怀孕了。目前建议所有孕妇,包括那些已经超重或肥胖的孕妇,尽量增加体重,不要减轻体重。
- 总是有吸收食物的问题(慢性吸收不良)
- 有胆囊问题(胆汁淤积)
- 对奥利司他或XENICAL 中的任何成分过敏。有关赛尼可成分的完整列表,请参阅本宣传册的末尾
在您服用XENICAL之前,请告诉您的医生您的所有健康状况,包括您是否
- 有肝脏问题
- 有肾脏问题
- 你的甲状腺有问题
- 有饮食问题,如厌食症或贪食症
- 有糖尿病
- 有癫痫症(癫痫)
- 有异常的心律(心律失常)
- 患有人类免疫缺陷病毒 (HIV)
- 正在母乳喂养或计划母乳喂养。不知道XENICAL 是否会进入您的母乳。在您进行母乳喂养并服用XENICAL之前,请咨询您的医生。
- 怀孕或计划怀孕。如果您怀孕或计划怀孕,请勿服用XENICAL。
告诉您的医生您服用的所有药物,包括处方药和非处方药、维生素和草药补充剂。
XENICAL和其他药物可能会相互影响导致副作用。XENICAL可能会影响其他药物的工作方式,而其他药物可能会影响XENICAL 的工作方式。
如果您正在服用以下药物,请特别告诉您的医生:
- 环孢素(Gengraf、Neoral、Sandimmune、Restasis、Sangcya)
- β-胡萝卜素或维生素 E 补充剂
- 左旋甲状腺素(Levo-T、Levolet、左旋甲状腺素、左旋甲状腺素钠、左旋甲状腺素、Novothyrox、Synthroid、Tirosint、Unithroid)。
- 华法林(凝血酶、凝血酶-K、香豆素、Jantoven、泛华芬、华法林钠)
- 胺碘酮(Cordarone、Pacerone)
- 用于治疗癫痫发作的药物。当您服用XENICAL时,它们可能效果不佳。如果您在服用XENICAL期间癫痫发作更频繁或变得更糟,请立即咨询您的医生。
- 用于治疗 HIV 的抗逆转录病毒药物。当您服用XENICAL时,它们可能效果不佳。
知道你吃的药。保留您的药物清单,并在您获得新药时将其展示给您的医生和药剂师。
我应该如何服用赛尼可?
- 完全按照医生的指示服用XENICAL。
- 您的医生会告诉您服用多少XENICAL以及何时服用。
- 饭后或饭后一小时内服用XENICAL。如果您错过了一顿饭或一顿没有脂肪的饭,您可以跳过您的XENICAL剂量。如果您服用环孢素药物,请至少间隔 3 小时服用XENICAL和环孢素。 请参阅“ 服用XENICAL前我应该告诉我的医生什么?” 环孢素药物的完整列表。
- 如果您服用复合维生素,请在服用XENICAL之前或之后至少服用 2 小时。就寝时间是服用多种维生素的好时机。
- 如果您服用左旋甲状腺素药物,请至少间隔 4 小时服用XENICAL和左旋甲状腺素。 请参阅“ 服用XENICAL前我应该告诉我的医生什么?” 有关左旋甲状腺素药物的完整列表。
- 以营养均衡、低热量的饮食服用XENICAL,其中脂肪的热量不超过约 30%。在任何高脂肪(超过 30% 脂肪)的膳食中服用XENICAL可能会使常见的副作用变得更糟。 请参阅 表1。

- 如果您服用过多的XENICAL,请立即致电您的医生或前往最近的医院急诊室。
XENICAL可能存在哪些风险?
XENICAL可能会导致严重的副作用,包括:
- 降低体内某些维生素的吸收。每天服用一次含有维生素 A、D、E、K 和 β-胡萝卜素的复合维生素。在服用XENICAL之前或之后至少 2 小时服用复合维生素,例如在睡前服用。
- 严重的肝脏问题。如果您有以下肝脏问题症状,请停止服用赛尼可并立即致电您的医生:
- 食欲不振
- 皮肤发痒
- 皮肤或眼睛的白色部分变黄
- 琥珀色尿液
- 浅色大便(大便)
- 胃右上部疼痛
- 肾脏问题。在XENICAL治疗期间,您的医生可能会进行某些检查以检查您的肾功能。如果您有以下肾脏问题症状,请立即致电您的医生:
- 肿胀,尤其是腿和脚
- 很少或没有尿量
- 尿频或疼痛
- 尿血
- 食欲不振、恶心和呕吐
- 背部、腹部或腹股沟剧烈疼痛
- 胆囊问题(胆结石)。如果您有以下胆结石症状,请立即致电您的医生:
- 胃右上部疼痛
- 恶心
- 呕吐
XENICAL最常见的副作用包括:
这些并不是XENICAL 的所有可能的副作用。
打电话给您的医生,征求有关副作用的医疗建议。您可以拨打 1-800-FDA-1088 向 FDA 报告副作用。
我应该如何储存XENICAL?
- 将XENICAL储存在 59°F 至 86°F(15°C 至 30°C)。
- 将XENICAL 保存在密闭容器中。
- 不要在瓶子上的有效期后使用XENICAL。
- 安全地扔掉过期或不再需要的药物。
将XENICAL和所有药物放在儿童接触不到的地方。
有关安全有效使用XENICAL 的一般信息。
有时会出于患者信息传单中列出的目的以外的目的开出药物。不要将XENICAL用于未规定的情况。不要将XENICAL给其他人,即使他们有与您相同的症状。这可能会伤害他们。
本患者信息手册总结了有关XENICAL的最重要信息。如果您想了解更多信息,请咨询您的医生。您可以向您的药剂师或医生咨询有关XENICAL 的信息,该信息是为健康专业人士编写的。
如需更多信息,请致电 1-888-236-5445 联系安全呼叫中心。
赛尼可的成分是什么?
活性成分:奥利司他
非活性成分:微晶纤维素、羟基乙酸淀粉钠、十二烷基硫酸钠、聚维酮、滑石、明胶和二氧化钛。
绿松石胶囊壳:FD&C Blue No. 2,黑色印刷油墨,含有药用级虫胶、丙二醇、强铵溶液、氢氧化钾和黑色氧化铁。
其他信息:体重指数
下图说明了根据各种体重和身高的体重指数 (BMI)。XENICAL适用于 BMI 大于或等于 30 kg/m 2或 BMI 大于或等于 27 kg/m 2且存在其他风险因素(如高血压、糖尿病或高胆固醇)的患者。BMI 的计算方法是将您的体重(公斤)除以您的身高(米)的平方。要使用此图表:
- 在左侧栏中找到与您的身高最接近的高度。
- 然后在顶行移动以找到最接近您体重的体重。
- 这两者相遇的数字是您的 BMI。(例如,体重 180 磅、身高 5 英尺 5 英寸的人的 BMI 为 30。)

本患者信息已获得美国食品和药物管理局的批准。
XENICAL ® 是CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH 的注册商标。
许可方:
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH
Ziegelhof 24, 17489 Greifswald, Germany
经销:
H2-Pharma, LLC , 2010 Berry Chase Place
Montgomery, AL 36117, USA
PPI 修订:08/2017
© 2017 CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH。
版权所有。油性分泌物可能是透明的或呈橙色或棕色。
标签的代表性样本(有关完整列表,请参阅 如何提供部分):
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 120 毫克胶囊瓶标签
国家数据中心 61269-460-90
赛尼可 ®
(奥利司他)120 毫克
每粒胶囊含有
120 毫克奥利司他。90粒
仅接收
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH
【备注】以上内容仅供参考,不作为用药依据,详情请参照药品附带说明书。
-
本说明书来源于:美国FDA
温馨提醒:
①建议您用 谷歌浏览器 在电脑上或手机 打开以上链接,就可以自动翻译成简体中文,而且翻译的还比较准确。
②本说明书仅供参考,最新的说明书详见药品附带的说明书
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XENICAL is indicated for obesity management including weight loss and weight maintenance when used in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet. XENICAL is also indicated to reduce the risk for weight regain after prior weight loss. XENICAL is indicated for obese patients with an initial body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m 2 or ≥27 kg/m 2 in the presence of other risk factors (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia).
Table 1 illustrates body mass index (BMI) according to a variety of weights and heights. The BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. For example, a person who weighs 180 lbs and is 5 '5 " would have a BMI of 30.

2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The recommended dose of XENICAL is one 120-mg capsule three times a day with each main meal containing fat (during or up to 1 hour after the meal).
The patient should be on a nutritionally balanced, reduced-calorie diet that contains approximately 30% of calories from fat. The daily intake of fat, carbohydrate, and protein should be distributed over three main meals. If a meal is occasionally missed or contains no fat, the dose of XENICAL can be omitted.
Because XENICAL has been shown to reduce the absorption of some fat-soluble vitamins and beta-carotene, patients should be counseled to take a multivitamin containing fat-soluble vitamins to ensure adequate nutrition [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . The vitamin supplement should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the administration of XENICAL, such as at bedtime.
For patients receiving both XENICAL and cyclosporine therapy, administer cyclosporine 3 hours after XENICAL.
For patients receiving both XENICAL and levothyroxine therapy, administer levothyroxine and XENICAL at least 4 hours apart. Patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine should be monitored for changes in thyroid function.
Doses above 120 mg three times a day have not been shown to provide additional benefit.
Based on fecal fat measurements, the effect of XENICAL is seen as soon as 24 to 48 hours after dosing. Upon discontinuation of therapy, fecal fat content usually returns to pretreatment levels within 48 to 72 hours.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
XENICAL 120 mg turquoise capsules imprinted with XENICAL 120 in black ink.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
XENICAL is contraindicated in:
- Pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
- Patients with chronic malabsorption syndrome
- Patients with cholestasis
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to XENICAL or to any component of this product
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Drug Interactions and Decreased Vitamin Absorption
XENICAL may interact with concomitant drugs including cyclosporine, levothyroxine, warfarin, amiodarone, antiepileptic drugs, and antiretroviral drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Data from a XENICAL and cyclosporine drug interaction study indicate a reduction in cyclosporine plasma levels when XENICAL was coadministered with cyclosporine. Therefore, XENICAL and cyclosporine should not be simultaneously coadministered. To reduce the chance of a drug-drug interaction, cyclosporine should be taken at least 3 hours before or after XENICAL in patients taking both drugs. In addition, in those patients whose cyclosporine levels are being measured, more frequent monitoring should be considered.
Patients should be strongly encouraged to take a multivitamin supplement that contains fat-soluble vitamins to ensure adequate nutrition because XENICAL has been shown to reduce the absorption of some fat-soluble vitamins and beta-carotene [see Dosage and Administration (2), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . In addition, the levels of vitamin D and beta-carotene may be low in obese patients compared with non-obese subjects. The supplement should be taken once a day at least 2 hours before or after the administration of XENICAL, such as at bedtime.
Weight-loss may affect glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus. A reduction in dose of oral hypoglycemic medication (e.g., sulfonylureas) or insulin may be required in some patients [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
5.2 Liver Injury
There have been rare postmarketing reports of severe liver injury with hepatocellular necrosis or acute hepatic failure in patients treated with XENICAL, with some of these cases resulting in liver transplant or death. Patients should be instructed to report any symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, light-colored stools, or right upper quadrant pain) while taking XENICAL. When these symptoms occur, XENICAL and other suspect medications should be discontinued immediately and liver function tests and ALT and AST levels obtained.
5.3 Increases in Urinary Oxalate
Some patients may develop increased levels of urinary oxalate following treatment with XENICAL. Cases of oxalate nephrolithiasis and oxalate nephropathy with renal failure have been reported. Monitor renal function when prescribing XENICAL to patients at risk for renal impairment and use with caution in those with a history of hyperoxaluria or calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis.
5.4 Cholelithiasis
Substantial weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis. In a clinical trial of XENICAL for the prevention of type 2 diabetes, the rates of cholelithiasis as an adverse event were 2.9% (47/1649) for patients randomized to XENICAL and 1.8% (30/1655) for patients randomized to placebo.
5.5 Miscellaneous
Organic causes of obesity (e.g., hypothyroidism) should be excluded before prescribing XENICAL.
Patients should be advised to adhere to dietary guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2)] . Gastrointestinal events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] may increase when XENICAL is taken with a diet high in fat (>30% total daily calories from fat). The daily intake of fat should be distributed over three main meals. If XENICAL is taken with any one meal very high in fat, the possibility of gastrointestinal effects increases.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in patients.
Commonly Observed (based on first year and second year data)
Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms were the most commonly observed treatment-emergent adverse events associated with the use of XENICAL in the seven double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials and are primarily a manifestation of the mechanism of action. (Commonly observed is defined as an incidence of ≥5% and an incidence in the XENICAL 120 mg group that is at least twice that of placebo.)

In general, the first occurrence of these events was within 3 months of starting therapy. Overall, approximately 50% of all episodes of GI adverse events associated with XENICAL treatment lasted for less than 1 week, and a majority lasted for no more than 4 weeks. However, GI adverse events may occur in some individuals over a period of 6 months or longer.
Discontinuation of Treatment
In controlled clinical trials, 8.8% of patients treated with XENICAL discontinued treatment due to adverse events, compared with 5.0% of placebo-treated patients. For XENICAL, the most common adverse events resulting in discontinuation of treatment were gastrointestinal.
Other Adverse Clinical Events
The following table lists other treatment-emergent adverse events from seven multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials that occurred at a frequency of ≥2% among patients treated with XENICAL 120 mg three times a day and with an incidence that was greater than placebo during year 1 and year 2, regardless of relationship to study medication.

Table 4 illustrates the percentage of adult patients on XENICAL and placebo who developed a low vitamin level on two or more consecutive visits during 1 and 2 years of therapy in studies in which patients were not previously receiving vitamin supplementation.

Table 5 illustrates the percentage of adolescent patients on XENICAL and placebo who developed a low vitamin level on two or more consecutive visits during the 1-year study.

In the 4-year XENDOS study, the general pattern of adverse events was similar to that reported for the 1- and 2-year studies with the total incidence of gastrointestinal-related adverse events occurring in year 1 decreasing each year over the 4-year period.
In clinical trials in obese diabetic patients, hypoglycemia and abdominal distension were also observed.
Pediatric Patients
In clinical trials with XENICAL in adolescent patients ages 12 to 16 years, the profile of adverse reactions was generally similar to that observed in adults.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of XENICAL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to XENICAL exposure.
- Rare cases of increase in transaminases and in alkaline phosphatase and hepatitis that may be serious have been reported. There have been reports of hepatic failure observed with the use of XENICAL in postmarketing surveillance, with some of these cases resulting in liver transplant or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
- Rare cases of hypersensitivity have been reported with the use of XENICAL. Signs and symptoms have included pruritus, rash, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm and anaphylaxis. Very rare cases of bullous eruption have been reported.
- Rare cases of leukocytoclastic vasculitis have been reported. Clinical signs include palpable purpura, maculopapular lesions, or bullous eruption.
- Acute oxalate nephropathy after treatment with XENICAL has been reported in patients with or at risk for renal disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
- Pancreatitis has been reported with the use of XENICAL in postmarketing surveillance. No causal relationship or physiopathological mechanism between pancreatitis and obesity therapy has been definitively established.
- Lower gastrointestinal bleeding has been reported in patients treated with XENICAL. Most reports are nonserious; severe or persistent cases should be investigated further.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cyclosporine
Data from a XENICAL and cyclosporine drug interaction study indicate a reduction in cyclosporine plasma levels when XENICAL was coadministered with cyclosporine. XENICAL and cyclosporine should not be simultaneously coadministered. Cyclosporine should be administered 3 hours after the administration of XENICAL [see Dosage and Administration (2), and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
7.2 Fat-soluble Vitamin Supplements and Analogues
Data from a pharmacokinetic interaction study showed that the absorption of beta-carotene supplement is reduced when concomitantly administered with XENICAL. XENICAL inhibited absorption of a vitamin E acetate supplement. The effect of XENICAL on the absorption of supplemental vitamin D, vitamin A, and nutritionally-derived vitamin K is not known at this time [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
7.3 Levothyroxine
Hypothyroidism has been reported in patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine postmarketing. Patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine should be monitored for changes in thyroid function. Administer levothyroxine and XENICAL at least 4 hours apart [see Dosage and Administration (2)] .
7.4 Anticoagulants including Warfarin
Vitamin K absorption may be decreased with XENICAL. Reports of decreased prothrombin, increased INR and unbalanced anticoagulant treatment resulting in change of hemostatic parameters have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and anticoagulants. Patients on chronic stable doses of warfarin or other anticoagulants who are prescribed XENICAL should be monitored closely for changes in coagulation parameters [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
7.5 Amiodarone
A pharmacokinetic study, where amiodarone was orally administered during orlistat treatment, demonstrated a reduction in exposure to amiodarone and its metabolite, desethylamiodarone [see Clinical Pharmocology (12.3)] . A reduced therapeutic effect of amiodarone is possible. The effect of commencing orlistat treatment in patients on stable amiodarone therapy has not been studied.
7.6 Antiepileptic Drugs
Convulsions have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with orlistat and antiepileptic drugs. Patients should be monitored for possible changes in the frequency and/or severity of convulsions.
7.7 Antiretroviral Drugs
Loss of virological control has been reported in HIV-infected patients taking orlistat concomitantly with antiretroviral drugs such as atazanavir, ritonavir, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, emtricitabine, and with the combinations lopinavir/ritonavir and emtricitabine/efavirenz/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. The exact mechanism for this is unclear, but may include a drug-drug interaction that inhibits systemic absorption of the antiretroviral drug. HIV RNA levels should be frequently monitored in patients who take XENICAL while being treated for HIV infection. If there is a confirmed increase in HIV viral load, XENICAL should be discontinued.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X
XENICAL is contraindicated during pregnancy, because weight loss offers no potential benefit to a pregnant woman and may result in fetal harm. A minimum weight gain, and no weight loss, is currently recommended for all pregnant women, including those who are already overweight or obese, due to the obligatory weight gain that occurs in maternal tissues during pregnancy. No embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was seen in animals that received orlistat at doses much higher than the recommended human dose. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard of maternal weight loss to the fetus.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies were conducted in rats and rabbits at doses up to 800 mg/kg/day. Neither study showed embryotoxicity or teratogenicity. This dose is 23 and 47 times the daily human dose calculated on a body surface area (mg/m 2) basis for rats and rabbits, respectively.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known if XENICAL is present in human milk. Caution should be exercised when XENICAL is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of XENICAL have been evaluated in obese adolescent patients aged 12 to 16 years. Use of XENICAL in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of XENICAL in adults with additional data from a 54-week efficacy and safety study and a 21-day mineral balance study in obese adolescent patients aged 12 to 16 years. Patients treated with XENICAL in the 54-week efficacy and safety study (64.8% female, 75% Caucasians, 18.8% Blacks, and 6.3% Other) had a mean reduction in BMI of 0.55 kg/m 2 compared with an average increase of 0.31 kg/m 2 in placebo-treated patients (p=0.001). In both adolescent studies, adverse effects were generally similar to those described in adults and included fatty/oily stool, oily spotting, and oily evacuation. In a subgroup of 152 XENICAL and 77 placebo patients from the 54-week study, changes in body composition measured by DEXA were similar in both treatment groups with the exception of fat mass, which was significantly reduced in patients treated with XENICAL compared to patients treated with placebo (-2.5 kg vs -0.6 kg, p=0.033). Because XENICAL can interfere with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, all patients should take a daily multivitamin that contains vitamins A, D, E, K, and beta-carotene. The vitamin supplement should be taken at least 2 hours before or after XENICAL [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
Plasma concentrations of orlistat and its metabolites M1 and M3 were similar to those found in adults at the same dose level. Daily fecal fat excretions were 27% and 7% of dietary intake in XENICAL and placebo treatment groups, respectively.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of XENICAL did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.2 Abuse
As with any weight-loss agent, the potential exists for abuse of XENICAL in inappropriate patient populations (e.g., patients with anorexia nervosa or bulimia). See Indications and Usage (1) for recommended prescribing guidelines.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Single doses of 800 mg XENICAL and multiple doses of up to 400 mg three times a day for 15 days have been studied in normal weight and obese subjects without significant adverse findings.
Should a significant overdose of XENICAL occur, it is recommended that the patient be observed for 24 hours. Based on human and animal studies, systemic effects attributable to the lipase-inhibiting properties of XENICAL should be rapidly reversible.
11 DESCRIPTION
XENICAL (orlistat) is a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor for obesity management that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats.
Orlistat is (S)-2-formylamino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid (S)-1-[[(2S, 3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl] methyl]-dodecyl ester. Its empirical formula is C 29H 53NO 5, and its molecular weight is 495.7. It is a single diastereomeric molecule that contains four chiral centers, with a negative optical rotation in ethanol at 529 nm. The structure is:

Orlistat is a white to off-white crystalline powder. Orlistat is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in chloroform, and very soluble in methanol and ethanol. Orlistat has no p Ka within the physiological pH range.
XENICAL is available for oral administration as a turquoise hard-gelatin capsule. The capsule is imprinted with black. Each capsule contains a pellet formulation consisting of 120 mg of the active ingredient, orlistat, as well as the inactive ingredients microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, sodium lauryl sulfate, povidone, and talc. The capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, and FD&C Blue No. 2 with black printing ink containing pharmaceutical grade shellac, propylene glycol, strong ammonium solution, potassium hydroxide and black iron oxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of gastrointestinal lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases. The inactivated enzymes are thus unavailable to hydrolyze dietary fat in the form of triglycerides into absorbable free fatty acids and monoglycerides. As undigested triglycerides are not absorbed, the resulting caloric deficit may have a positive effect on weight control.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Dose-response Relationship
The dose-response relationship for orlistat in human volunteers is shown in Figure 1. The effect is the percentage of ingested fat excreted, referred to as fecal fat excretion percentage. Both individual data (open circles) and the curve predicted for the population with the maximum-effect model (continuous line) are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Dose-Response Relationship for Orlistat in Human Volunteers

At the recommended therapeutic dose of 120 mg three times a day, orlistat inhibits dietary fat absorption by approximately 30%.
Ethanol does not affect orlistat's effect on preventing the absorption of fat.
Other Short-term Studies
Adults
In several studies of up to 6-weeks duration, the effects of therapeutic doses of XENICAL on gastrointestinal and systemic physiological processes were assessed in normal weight and obese subjects. Postprandial cholecystokinin plasma concentrations were lowered after multiple doses of XENICAL in two studies but not significantly different from placebo in two other experiments. There were no clinically significant changes observed in gallbladder motility, bile composition or lithogenicity, or colonic cell proliferation rate, and no clinically significant reduction of gastric emptying time or gastric acidity. In addition, no effects on plasma triglyceride levels or systemic lipases were observed with the administration of XENICAL in these studies. In a 3-week study of 28 healthy male volunteers, XENICAL (120 mg three times a day) did not significantly affect the balance of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, copper, and iron.
Pediatrics
In a 3-week study of 32 obese adolescents aged 12 to 16 years, XENICAL (120 mg three times a day) did not significantly affect the balance of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, or copper. The iron balance was decreased by 64.7 µmole/24 hours and 40.4 µmole/24 hours in XENICAL and placebo treatment groups, respectively.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Systemic exposure to orlistat is minimal. Following oral dosing with 360 mg 14C-orlistat, plasma radioactivity peaked at approximately 8 hours; plasma concentrations of intact orlistat were near the limits of detection (<5 ng/mL). In therapeutic studies involving monitoring of plasma samples, detection of intact orlistat in plasma was sporadic and concentrations were low (<10 ng/mL or 0.02 µM), without evidence of accumulation, and consistent with minimal absorption.
Distribution
In vitro orlistat was >99% bound to plasma proteins (lipoproteins and albumin were major binding proteins). Orlistat minimally partitioned into erythrocytes.
Metabolism
Based on an oral 14C-orlistat mass balance study in obese patients, two metabolites, M1 ((the hydrolyzed β-lactone ring product of orlistat) and M3 (sequential metabolite after M1's cleavage of the N-formyl leucine side-chain), accounted for approximately 42% of total radioactivity in plasma. M1 and M3 have an open β-lactone ring and extremely weak lipase inhibitory activity (1000- and 2500-fold less than orlistat, respectively). In view of this low inhibitory activity and the low plasma levels at the therapeutic dose (average of 26 ng/mL and 108 ng/mL for M1 and M3, respectively, 2 to 4 hours after a dose), these metabolites are considered pharmacologically inconsequential. The primary metabolite M1 had a short half-life (approximately 3 hours) whereas the secondary metabolite M3 eliminated at a slower rate (half-life approximately 13.5 hours).
Elimination
Following a single oral dose of 360 mg 14C-orlistat in both normal weight and obese subjects, fecal excretion of the unabsorbed drug was found to be the major route of elimination. Orlistat and its M1 and M3 metabolites were also subject to biliary excretion. Approximately 97% of the administered radioactivity was excreted in feces; 83% of that was found to be unchanged orlistat. The cumulative renal excretion of total radioactivity was <2% of the given dose of 360 mg 14C-orlistat. The time to reach complete excretion (fecal plus urinary) was 3 to 5 days. The disposition of orlistat appeared to be similar between normal weight and obese subjects. Based on limited data, the half-life of the absorbed orlistat is in the range of 1 to 2 hours.
Specific Populations
No pharmacokinetic study was conducted for specific populations such as geriatric, different races, and patients with renal and hepatic impairment.
Drug Interactions
Alcohol
In a multiple-dose study in 30 normal-weight subjects, coadministration of XENICAL and 40 grams of alcohol (e.g., approximately 3 glasses of wine) did not result in alteration of alcohol pharmacokinetics, orlistat pharmacodynamics (fecal fat excretion), or systemic exposure to orlistat.
Amiodarone
In a pharmacokinetic study conducted in healthy volunteers who received 120 mg orlistat three times daily for 13 days and a single dose of 120 mg orlistat on the morning of Day 14 co-administered with a single dose of 1200 mg amiodarone on Day 4, a 23 – 27% reduction in the systemic exposure to amiodarone and desethylamiodarone was observed [see Drug Interactions (7.5)] . The effect of commencing orlistat treatment in patients on stable amiodarone therapy has not been studied.
Cyclosporine
In a multiple-dose study, coadministration of 50 mg cyclosporine twice daily with 120 mg XENICAL three times daily decreased cyclosporine AUC and C max by 31% and 25%, respectively. In the same study, administration of 50 mg cyclosporine twice daily three hours after the administration of 120 mg XENICAL three times daily decreased cyclosporine AUC and C max by 17% and 4%, respectively.
Digoxin
In 12 normal-weight subjects receiving XENICAL 120 mg three times a day for 6 days, XENICAL did not alter the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of digoxin.
Fat-soluble Vitamin Supplements and Analogues
A pharmacokinetic interaction study showed a 30% reduction in beta-carotene supplement absorption when concomitantly administered with XENICAL. XENICAL inhibited absorption of a vitamin E acetate supplement by approximately 60%. The effect of XENICAL on the absorption of supplemental vitamin D, vitamin A, and nutritionally-derived vitamin K is not known at this time.
Glyburide
In 12 normal-weight subjects receiving orlistat 80 mg three times a day for 5 days, orlistat did not alter the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics (blood glucose-lowering) of glyburide.
Nifedipine (extended-release tablets)
In 17 normal-weight subjects receiving XENICAL 120 mg three times a day for 6 days, XENICAL did not alter the bioavailability of nifedipine (extended-release tablets).
Oral Contraceptives
In 20 normal-weight female subjects, the treatment of XENICAL 120 mg three times a day for 23 days resulted in no changes in the ovulation-suppressing action of oral contraceptives.
Phenytoin
In 12 normal-weight subjects receiving XENICAL 120 mg three times a day for 7 days, XENICAL did not alter the pharmacokinetics of a single 300-mg dose of phenytoin.
Pravastatin
In a 2-way crossover study of 24 normal-weight, mildly hypercholesterolemic patients receiving XENICAL 120 mg three times a day for 6 days, XENICAL did not affect the pharmacokinetics of pravastatin.
Warfarin
In 12 normal-weight subjects, administration of XENICAL 120 mg three times a day for 16 days did not result in any change in either warfarin pharmacokinetics (both R- and S-enantiomers) or pharmacodynamics (prothrombin time and serum Factor VII). Although undercarboxylated osteocalcin, a marker of vitamin K nutritional status, was unaltered with XENICAL administration, vitamin K levels tended to decline in subjects taking XENICAL. Therefore, as vitamin K absorption may be decreased with XENICAL, patients on chronic stable doses of warfarin who are prescribed XENICAL should be monitored closely for changes in coagulation parameters.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice did not show a carcinogenic potential for orlistat at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day and 1500 mg/kg/day, respectively. For mice and rats, these doses are 38 and 46 times the daily human dose calculated on an area under concentration vs time curve basis of total drug-related material.
Orlistat had no detectable mutagenic or genotoxic activity as determined by the Ames test, a mammalian forward mutation assay (V79/HPRT), an in vitro clastogenesis assay in peripheral human lymphocytes, an unscheduled DNA synthesis assay (UDS) in rat hepatocytes in culture, and an in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
When given to rats at a dose of 400 mg/kg/day in a fertility and reproduction study, orlistat had no observable adverse effects. This dose is 12 times the daily human dose calculated on a body surface area (mg/m 2) basis.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The long-term effects of XENICAL on morbidity and mortality associated with obesity have not been established.
The effects of XENICAL on weight loss, weight maintenance, and weight regain and on a number of comorbidities (e.g., type 2 diabetes, lipids, blood pressure) were assessed in the 4-year XENDOS study and in seven long-term (1- to 2-years duration) multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. During the first year of therapy, the studies of 2-year duration assessed weight loss and weight maintenance. During the second year of therapy, some studies assessed continued weight loss and weight maintenance and others assessed the effect of XENICAL on weight regain. These studies included over 2800 patients treated with XENICAL and 1400 patients treated with placebo (age range 17-78 years, 80.2% women, 91.0% Caucasians, 5.7% Blacks, 2.3% Hispanics, 0.9% Other). The majority of these patients had obesity-related risk factors and comorbidities. In the XENDOS study, which included 3304 patients (age range 30-58 years, 55% women, 99% Caucasians, 1% other), the time to onset of type 2 diabetes was assessed in addition to weight management. In all these studies, treatment with XENICAL and placebo designates treatment with XENICAL plus diet and placebo plus diet, respectively.
During the weight loss and weight maintenance period, a well-balanced, reduced-calorie diet that was intended to result in an approximate 20% decrease in caloric intake and provide 30% of calories from fat was recommended to all patients. In addition, all patients were offered nutritional counseling.
14.1 One-year Results: Weight Loss, Weight Maintenance, and Risk Factors
Pooled data from five clinical trials indicated that the overall mean weight loss from randomization to the end of 1 year of treatment in the intent-to-treat population was 13.4 lbs in the patients treated with XENICAL and 5.8 lbs in the placebo-treated patients. After 1 year of treatment, the mean percent weight loss difference between XENICAL-treated patients and placebo-treated patients was 3%. One thousand seventy two (69%) patients treated with XENICAL and 701 (63%) patients treated with placebo completed 1 year of treatment. Of the patients who completed 1 year of treatment, 57% of the patients treated with XENICAL (120 mg three times a day) and 31% of the placebo-treated patients lost at least 5% of their baseline body weight.
The percentages of patients achieving ≥5% and ≥10% weight loss after 1 year in five large multicenter studies for the intent-to-treat populations are presented in Table 6.

The relative changes in risk factors associated with obesity following 1 year of therapy with XENICAL and placebo are presented for the population as a whole and for the population with abnormal values at randomization.
Population as a Whole
The changes in metabolic, cardiovascular and anthropometric risk factors associated with obesity based on pooled data for five clinical studies, regardless of the patient's risk factor status at randomization, are presented in Table 7. One year of therapy with XENICAL resulted in relative improvement in several risk factors.

Population With Abnormal Risk Factors at Randomization
The changes from randomization following 1-year treatment in the population with abnormal lipid levels (LDL ≥130 mg/dL, LDL/HDL ≥3.5, HDL <35 mg/dL) were greater for XENICAL compared to placebo with respect to LDL-cholesterol (-7.83% vs +1.14%) and the LDL/HDL ratio (-0.64 vs -0.46). HDL increased in the placebo group by 20.1% and in the XENICAL group by 18.8%. In the population with abnormal blood pressure at baseline (systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg), the change in SBP from randomization to 1 year was greater for XENICAL (-10.89 mm Hg) than placebo (-5.07 mm Hg). For patients with a diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg, XENICAL patients decreased by -7.9 mm Hg while the placebo patients decreased by -5.5 mm Hg. Fasting insulin decreased more for XENICAL than placebo (-39 vs -16 pmol/L) from randomization to 1 year in the population with abnormal baseline values (≥120 pmol/L). A greater reduction in waist circumference for XENICAL vs placebo (-7.29 vs -4.53 cm) was observed in the population with abnormal baseline values (≥100 cm).
14.2 Effect on Weight Regain
Three studies were designed to evaluate the effects of XENICAL compared to placebo in reducing weight regain after a previous weight loss achieved following either diet alone (one study, 14302) or prior treatment with XENICAL (two studies, 14119C and 14185). The diet utilized during the 1-year weight regain portion of the studies was a weight-maintenance diet, rather than a weight-loss diet, and patients received less nutritional counseling than patients in weight-loss studies. For studies 14119C and 14185, patients' previous weight loss was due to 1 year of treatment with XENICAL in conjunction with a mildly hypocaloric diet. Study 14302 was conducted to evaluate the effects of 1 year of treatment with XENICAL on weight regain in patients who had lost 8% or more of their body weight in the previous 6 months on diet alone.
In study 14119C, patients treated with placebo regained 52% of the weight they had previously lost while the patients treated with XENICAL regained 26% of the weight they had previously lost (p<0.001). In study 14185, patients treated with placebo regained 63% of the weight they had previously lost while the patients treated with XENICAL regained 35% of the weight they had lost (p<0.001). In study 14302, patients treated with placebo regained 53% of the weight they had previously lost while the patients treated with XENICAL regained 32% of the weight that they had lost (p<0.001).
14.3 Two-year Results: Long-term Weight Control and Risk Factors
The treatment effects of XENICAL were examined for 2 years in four of the five 1-year weight management clinical studies previously discussed (see Table 6). At the end of year 1, the patients' diets were reviewed and changed where necessary. The diet prescribed in the second year was designed to maintain patient's current weight. XENICAL was shown to be more effective than placebo in long-term weight control in four large, multicenter, 2-year double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.
Pooled data from four clinical studies indicate that 74% of all patients treated with 120 mg three times a day of XENICAL and 76% of patients treated with placebo completed 2 years of the same therapy. Pooled data from four clinical studies indicate that the mean weight loss difference between XENICAL 120 mg three times a day and placebo treatment groups at year 2 in those patients who completed 1 year of treatment (ITT LOCF) was 3%. In the same studies cited in the One-year Results (see Table 6), the percentages of patients achieving a ≥5% and ≥10% weight loss after 2 years are shown in Table 8.

The relative changes in risk factors associated with obesity following 2 years of therapy were also assessed in the population as a whole and the population with abnormal risk factors at randomization.
Population as a Whole
The relative differences in risk factors between treatment with XENICAL and placebo were similar to the results following 1 year of therapy for total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, LDL/HDL ratio, triglycerides, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, diastolic blood pressure, waist circumference, and hip circumference. The relative differences between treatment groups for HDL cholesterol and systolic blood pressure were less than that observed in the year one results.
Population With Abnormal Risk Factors at Randomization
The relative differences in risk factors between treatment with XENICAL and placebo were similar to the results following 1 year of therapy for LDL- and HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting insulin, diastolic blood pressure, and waist circumference. The relative differences between treatment groups for LDL/HDL ratio and isolated systolic blood pressure were less than that observed in the year one results.
14.4 Four-year Results: Long-term Weight Control and Risk Factors
In the 4-year double-blind, placebo-controlled XENDOS study, the effects of XENICAL in delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes and on body weight were compared to placebo in 3304 obese patients who had either normal or impaired glucose tolerance at baseline. Thirty-four percent of the 1655 patients who were randomized to the placebo group and 52% of the 1649 patients who were randomized to the XENICAL group completed the 4-year study.
At the end of the study, the mean percent weight loss in the placebo group was -2.75% compared with -5.17% in the XENICAL group (p<0.001) (see Figure 2). Forty-five percent of the placebo patients and 73% of the XENICAL patients lost ≥5% of their baseline body weight, and 21% of the placebo patients and 41% of the XENICAL patients lost ≥10% of their baseline body weight following the first year of treatment. Following 4 years of treatment, 28% of the placebo patients and 45% of the XENICAL patients lost ≥5% of their baseline body weight and 10% of the placebo patients and 21% of the XENICAL patients lost ≥10% of their baseline body weight. After 4 years of treatment, the mean % difference in weight loss between XENICAL treated patients and placebo was 2.5%.
Figure 2 Mean Change from Baseline Body Weight (Kgs) Over Time*

*ITT LOCF study population
The relative changes from baseline in risk factors associated with obesity following 4 years of therapy were assessed in the XENDOS study population (see Table 9).

Onset of Type 2 Diabetes in Obese Patients
In the XENDOS trial, in the overall population, XENICAL delayed the onset of type 2 diabetes such that at the end of four years of treatment the cumulative incidence rate of diabetes was 8.3% for the placebo group compared to 5.5% for the XENICAL group, p=0.01 (see Table 10). This finding was driven by a statistically-significant reduction in the incidence of developing type 2 diabetes in those patients who had impaired glucose tolerance at baseline ( Table 10 and Figure 3). XENICAL did not reduce the risk for the development of diabetes in patients with normal glucose tolerance at baseline.
The effect of XENICAL to delay the onset of type 2 diabetes in obese patients with IGT is presumably due to weight loss, and not to any independent effects of the drug on glucose or insulin metabolism. The effect of XENICAL on weight loss is adjunctive to diet and exercise.

Figure 3 Percentage of Patients Without Diabetes Over Time

14.5 Study of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
A 1-year double-blind, placebo-controlled study in type 2 diabetics (N=321) stabilized on sulfonylureas was conducted. Thirty percent of patients treated with XENICAL achieved at least a 5% or greater reduction in body weight from randomization compared to 13% of the placebo-treated patients (p<0.001). Table 11 describes the changes over 1 year of treatment with XENICAL compared to placebo, in sulfonylurea usage and dose reduction as well as in hemoglobin HbA1c, fasting glucose, and insulin.

In addition, XENICAL (n=162) compared to placebo (n=159) was associated with significant lowering for total cholesterol (-1.0% vs +9.0%, p≤0.05), LDL-cholesterol (-3.0% vs +10.0%, p≤0.05), LDL/HDL ratio (-0.26 vs -0.02, p≤0.05) and triglycerides (+2.54% vs +16.2%, p≤0.05), respectively. For HDL cholesterol, there was a +6.49% increase on XENICAL and +8.6% increase on placebo, p>0.05. Systolic blood pressure increased by +0.61 mm Hg on XENICAL and increased by +4.33 mm Hg on placebo, p>0.05. Diastolic blood pressure decreased by -0.47 mm Hg for XENICAL and by -0.5 mm Hg for placebo, p>0.05.
14.6 Glucose Tolerance in Obese Patients
Two-year studies that included oral glucose tolerance tests were conducted in obese patients not previously diagnosed or treated for type 2 diabetes and whose baseline oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) status at randomization was either normal, impaired, or diabetic.
The progression from a normal OGTT at randomization to a diabetic or impaired OGTT following 2 years of treatment with XENICAL (n=251) or placebo (n=207) were compared. Following treatment with XENICAL, 0.0% and 7.2% of the patients progressed from normal to diabetic and normal to impaired, respectively, compared to 1.9% and 12.6% of the placebo treatment group, respectively.
In patients found to have an impaired OGTT at randomization, the percent of patients improving to normal or deteriorating to diabetic status following 1 and 2 years of treatment with XENICAL compared to placebo are presented. After 1 year of treatment, 45.8% of the placebo patients and 73% of the XENICAL patients had a normal oral glucose tolerance test while 10.4% of the placebo patients and 2.6% of the XENICAL patients became diabetic. After 2 years of treatment, 50% of the placebo patients and 71.7% of the XENICAL patients had a normal oral glucose tolerance test while 7.5% of placebo patients were found to be diabetic and 1.7% of XENICAL patients were found to be diabetic after treatment.
14.7 Pediatric Clinical Studies
The effects of XENICAL on body mass index (BMI) and weight loss were assessed in a 54-week multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 539 obese adolescents (357 receiving XENICAL 120 mg three times a day, 182 receiving placebo), aged 12 to 16 years. All study participants had a baseline BMI that was 2 units greater than the US weighted mean for the 95 th percentile based on age and gender. Body mass index was the primary efficacy parameter because it takes into account changes in height and body weight, which occur in growing children.
During the study, all patients were instructed to take a multivitamin containing fat-soluble vitamins at least 2 hours before or after ingestion of XENICAL. Patients were also maintained on a well-balanced, reduced-calorie diet that was intended to provide 30% of calories from fat. In addition, all patients were placed on a behavior modification program and offered exercise counseling.
Approximately 65% of patients in each treatment group completed the study.
Following one year of treatment, BMI decreased by an average of 0.55 kg/m 2 in the XENICAL-treated patients and increased by an average of 0.31 kg/m 2 in the placebo-treated patients (p=0.001).
The percentages of patients achieving ≥5% and ≥10% reduction in BMI and body weight after 52 weeks of treatment for the intent-to-treat population are presented in Table 12.

16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
XENICAL is a turquoise, hard-gelatin capsule containing pellets of powder.
XENICAL 120 mg Capsules: Turquoise, two-piece, No. 1 opaque hard-gelatin capsule imprinted with XENICAL 120 in black ink — bottle of 90 (NDC 61269-460-90).
Storage and Handling
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep bottle tightly closed.
XENICAL should not be used after the given expiration date.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Information for Patients
Patients should not take XENICAL if they are pregnant, have chronic malabsorption syndrome, cholestasis or hypersensitivity to XENICAL or to any component of this product [see Contraindications (4)] .
Concomitant Medications
Patients should be asked if they are taking cyclosporine, beta carotene or vitamin E supplements, levothyroxine, warfarin, antiepileptic drugs, amiodarone, or antiretroviral drugs due to potential interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)] .
Commonly Observed Adverse Events
Patients should be informed of the commonly-observed adverse events associated with the use of XENICAL which include oily spotting, flatus with discharge, fecal urgency, fatty/oily stool, oily evacuation, increased defecation, fecal incontinence [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
Potential Risks and Benefits
Patients should be informed of potential risks which include lowered absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and potential liver injury, increases in urinary oxalate, and cholelithiasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5)] . Treatment with XENICAL may result in weight loss and improvement in obesity-related risk factors due to weight loss [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
Dosing Instructions
Patients should be counseled to take XENICAL as directed with meals or up to one hour after a meal. Patients should also be advised to take multivitamin supplementation at least two hours before or after the administration of XENICAL, or at bedtime [see Dosage and Administration (2)] .
XENICAL® is a registered trademark of CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH.
Licensed by:
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH
Ziegelhof 24
17489 Greifswald, Germany
Distributed by:
H2-Pharma, LLC
2010 Berry Chase Place
Montgomery, AL 36117, USA
© 2017 CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH. All rights reserved.Patient Information
XENICAL ® (zen´i-cal)
(orlistat)
CapsulesRead this Patient Information before you start taking XENICAL and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is XENICAL?
XENICAL is a prescription medicine used with a low calorie diet to increase weight loss in people with obesity. XENICAL may help obese people lose weight and keep the weight off.
It is not known if XENICAL is safe and effective in children under 12 years old.
Who should not take XENICAL?
Do not take XENICAL if you:
- are pregnant. A minimum weight gain, and no weight loss, is currently recommended for all pregnant women, including those who are already overweight or obese.
- always have problems absorbing food (chronic malabsorption)
- have gallbladder problems (cholestasis)
- are allergic to orlistat or any of the ingredients in XENICAL. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in XENICAL
Before you take XENICAL, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- have problems with your thyroid
- have eating problems such as anorexia or bulimia
- have diabetes
- have a seizure disorder (epilepsy)
- have an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia)
- have the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if XENICAL passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor before you breastfeed and take XENICAL.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Do not take XENICAL if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
XENICAL and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. XENICAL may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect the way XENICAL works.
Especially tell your doctor if you are taking:
- cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune, Restasis, Sangcya)
- beta-carotene or vitamin E supplements
- levothyroxine (Levo-T, Levolet, Levothyroid, Levothyroxine Sodium, Levoxyl, Novothyrox, Synthroid, Tirosint, Unithroid).
- warfarin (Athrombin, Athrombin-K, Coumadin, Jantoven, Panwarfin, Warfarin Sodium)
- amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone)
- medicines used to treat seizures. They may not work as well while you take XENICAL. Talk to your doctor right away if your seizures happen more often or get worse while you take XENICAL.
- antiretroviral medicines used to treat HIV. They may not work as well while you take XENICAL.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take XENICAL?
- Take XENICAL exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor will tell you how much XENICAL to take and when to take it.
- Take XENICAL with your meals or up to one hour after your meal. If you miss a meal or have a meal without fat, you can skip your dose of XENICAL. If you take a cyclosporine medicine, take XENICAL and cyclosporine at least 3 hours apart. See " What should I tell my doctor before taking XENICAL?" for a complete list of cyclosporine medicines.
- If you take a multivitamin, take it at least 2 hours before or after you take XENICAL. Bedtime is a good time to take your multivitamin.
- If you take a levothyroxine medicine, take XENICAL and levothyroxine at least 4 hours apart. See " What should I tell my doctor before taking XENICAL?" for a complete list of levothyroxine medicines.
- Take XENICAL with a nutritionally balanced, low calorie diet that has no more than about 30% of calories from fat. Taking XENICAL with any meal high in fat (more than 30% fat) may make the common side effects worse. See Table 1.

- If you take too much XENICAL call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible risks of XENICAL?
XENICAL may cause serious side effects, including:
- Lowered absorption of certain vitamins in your body. Take a multivitamin containing vitamins A, D, E, K, and beta-carotene one time each day. Take a multivitamin at least 2 hours before or after you take XENICAL, such as at bedtime.
- Severe liver problems. Stop taking XENICAL and call your doctor right away if you have the following symptoms of liver problems:
- loss of appetite
- itchy skin
- yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes
- amber-colored urine
- light-colored bowel movements (stools)
- pain in the upper right portion of your stomach
- Kidney problems. Your doctor may do certain tests to check your kidney function during treatment with XENICAL. Call your doctor right away if you have the following symptoms of kidney problems:
- swelling, especially of the legs and feet
- little or no urine output
- frequent or painful urination
- blood in the urine
- loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting
- severe pain in the back, belly or groin
- Gallbladder problems (gallstones). Call your doctor right away if you have the following symptoms of gallstones:
- pain in the upper right portion of your stomach
- nausea
- vomiting
The most common side effects of XENICAL include:
- oily 1 rectal discharge
- passing gas with oily discharge 1
- urgent need to have a bowel movement
- oily 1 or fatty stools
- increased number of bowel movements
- being unable to control your bowel movements
These are not all the possible side effects of XENICAL.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store XENICAL?
- Store XENICAL at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep XENICAL in a tightly closed container.
- Do not use XENICAL after the expiration date on the bottle.
- Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep XENICAL and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of XENICAL.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use XENICAL for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give XENICAL to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about XENICAL. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about XENICAL that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call the Safety Call Center at 1-888-236-5445.
What are the ingredients in XENICAL?
Active Ingredient: orlistat
Inactive Ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, sodium lauryl sulfate, povidone, talc, gelatin and titanium dioxide.
Turquoise capsule shell: FD&C Blue No. 2, with black printing ink containing pharmaceutical grade shellac, propylene glycol, strong ammonium solution, potassium hydroxide and black iron oxide.
Other Information: Body Mass Index
The chart below illustrates body mass index (BMI) according to a variety of weights and heights. XENICAL is intended for patients with a BMI of greater than or equal to 30 kg/m 2 or a BMI of greater than or equal to 27 kg/m 2 in the presence of other risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or high cholesterol. The BMI is calculated by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. To use this chart:
- Find the height closest to your height in the left-hand column.
- Then move across the top row to find the weight closest to your weight.
- The number where these two meet is your BMI. (For example, a person who weighs 180 lbs and is 5'5" has a BMI of 30.)

This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
XENICAL® is a registered trademark of CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH.
Licensed by:
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH
Ziegelhof 24, 17489 Greifswald, Germany
Distributed by:
H2-Pharma, LLC, 2010 Berry Chase Place
Montgomery, AL 36117, USA
PPI Revised: 08/2017
© 2017 CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH.
All rights reserved.Oily discharge may be clear or have an orange or brown color.
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 120 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 61269-460-90
Xenical ®
(orlistat)120 mg
Each capsule contains
120 mg orlistat.90 capsules
Rx only
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH

【备注】以上内容仅供参考,不作为用药依据,详情请参照药品附带说明书。
-
搜索更多相关资讯,请进入资讯页面
